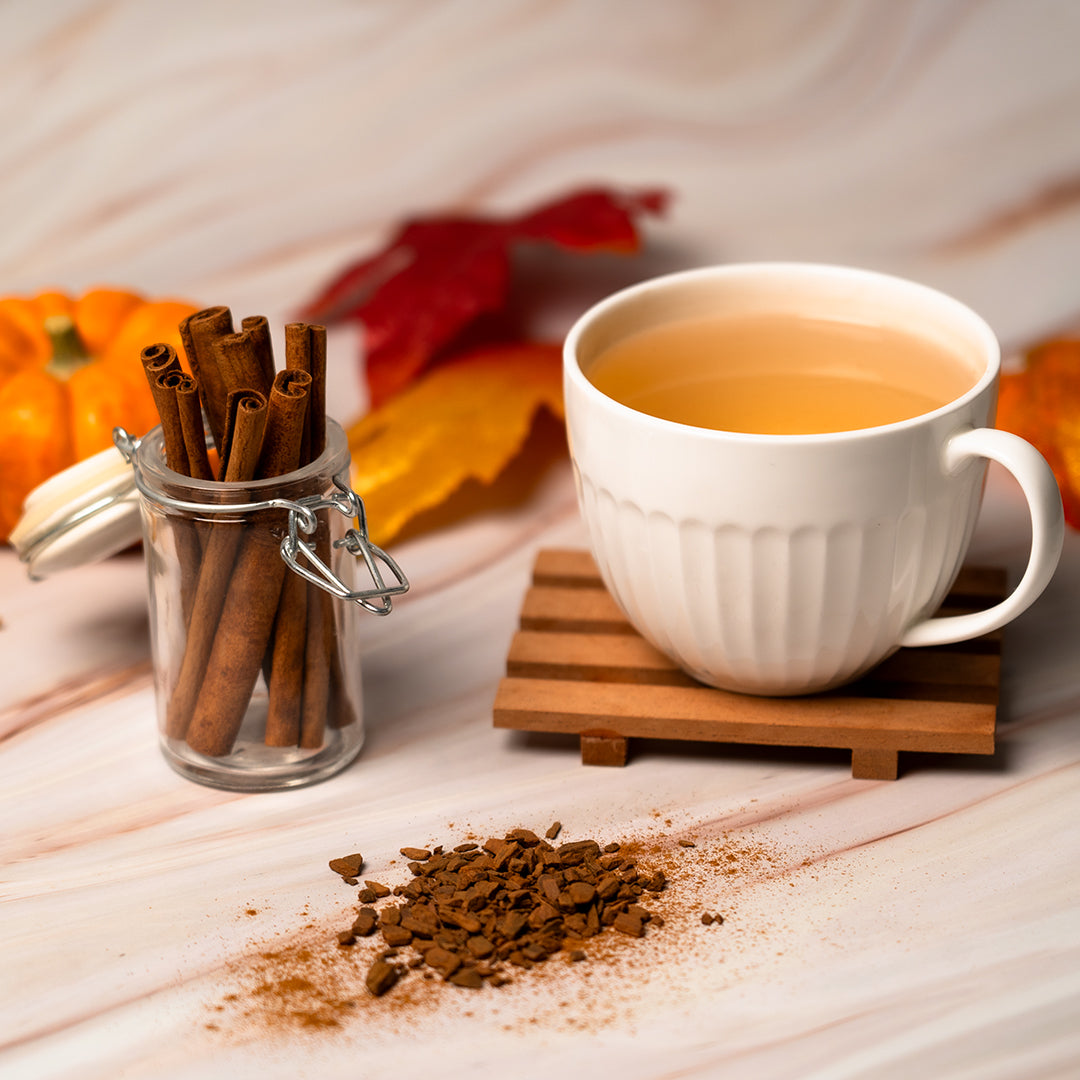
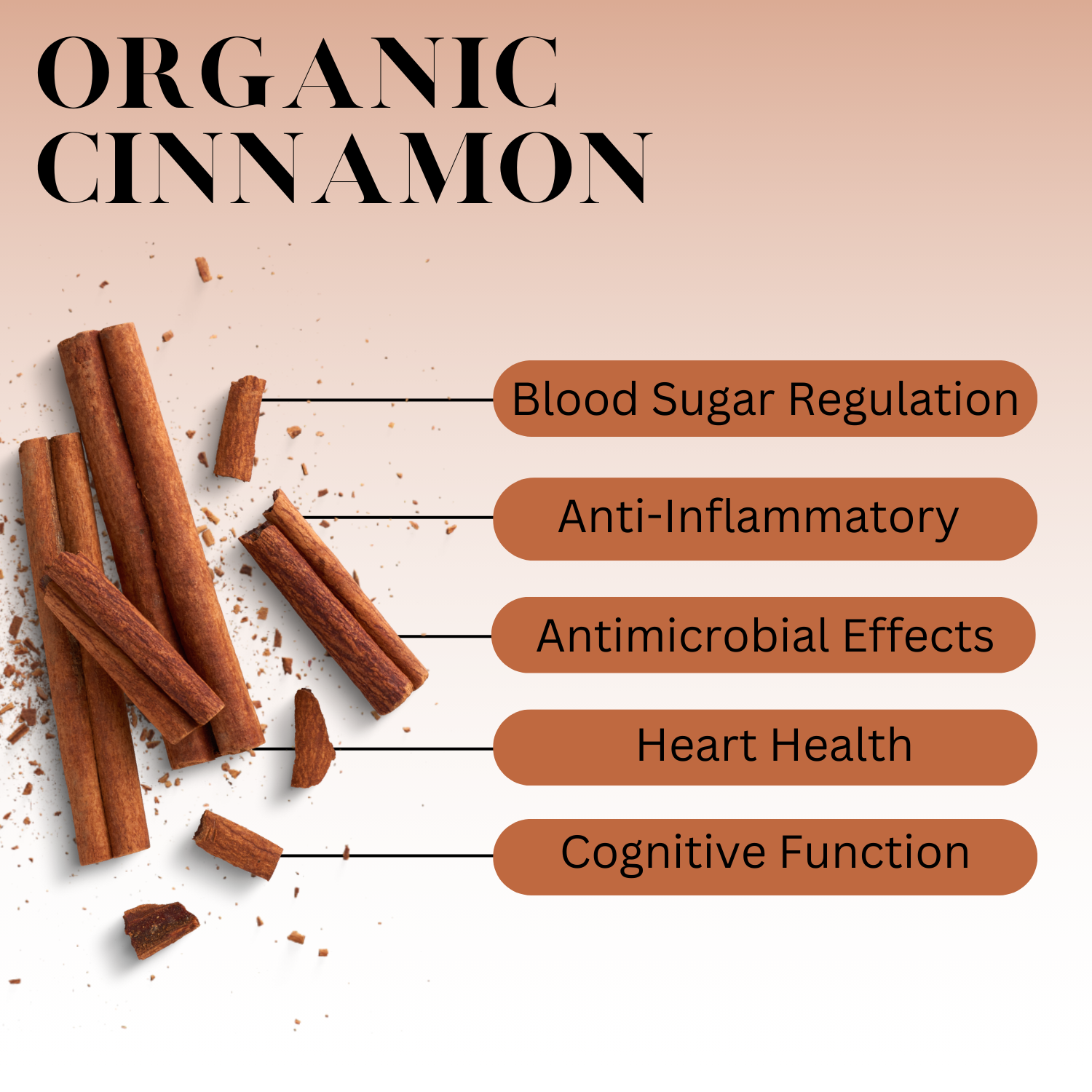
What Exactly Is Cinnamon?

Cinnamon comes from the inner bark of evergreen trees in the Cinnamomum genus. Two species dominate the spice trade, each offering distinct characteristics that have shaped culinary traditions worldwide.
The signature scent and sweet warmth come from the oil cinnamaldehyde, which makes up 60–75% of cinnamon's volatile compounds.